Oxalic acid is a crystalline organic substance found naturally in many plants and foods. The oxalic acid and the oxalate crystals that it forms can irritate the tissues of the body or even form stones. Here are some organs that can be affected by oxalates:
kidneys: kidney stones can form from oxalates and are called oxalate stones. This typically occurs in people who are eating foods high in oxalates and not drinking enough water.
bladder: intestitial cystitis (inflammation of the bladder) can be caused by oxalates/oxalic acid. The symptoms are similar to a bladder infection (urgent need to urinate, urinating often, bladder or pelvic pain) but without the presence of bacteria in the urine.
lungs: low lung function and even asthmatic type symptoms can be attributed to oxalic acid. it was found that levels of oxalic acid is often high in the bronchi of people with certain pulmonary conditions
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4051310
What food are high in oxalates?
Spinach: if you steam or otherwise cook spinach and other greens, the oxalic acid dissolves and does not create problems. The trouble happens when people are eating alot of raw spinach, other raw greens. This can especially happen when people put fresh greens in their smoothies or drink juiced greens. I do not recommend doing green smoothies. Many of my patients who do these end up being sensitive to oxalates--especially children. An adult friend of mine did get oxalate kidney stones. He ate spinach salad every dinner and did not drink any water--he preferred soda and beer. If he had drank alot of water, he may have avoided the stones.
Beet greens (remember to cook them)
Collard greens (cooking them breaks down the oxalic acid)
Parsley
Chives
Cassava
Amaranth
Radish
Carrots
Beans, dried
Rhubarb
Wheat bran
Strawberries
Almonds (some sources state)
sesame (some sources state)
Remember, these foods are not dangerous, but they do contain high levels of oxalic acid. If not cooked or if consumed in large quantities, the crystals could cause trouble in the body. A study was done to determine the effect of cooking on removing oxalates from food:
J Agric Food Chem. 2005 Apr 20;53(8):3027-30.
Effect of different cooking methods on vegetable oxalate content.
Source
Department of Family and Consumer Sciences (Nutrition), Department 3354, University of Wyoming, 1000 East University Avenue, Laramie, Wyoming 82071, USA.
Abstract
Approximately 75% of all kidney stones are composed primarily of calcium oxalate, and hyperoxaluria is a primary risk factor for this disorder. Nine types of raw and cooked vegetables were analyzed for oxalate using an enzymatic method. There was a high proportion of water-soluble oxalate in most of the tested raw vegetables. Boiling markedly reduced soluble oxalate content by 30-87% and was more effective than steaming (5-53%) and baking (used only for potatoes, no oxalate loss). An assessment of the oxalate content of cooking water used for boiling and steaming revealed an approximately 100% recovery of oxalate losses. The losses of insoluble oxalate during cooking varied greatly, ranging from 0 to 74%. Because soluble sources of oxalate appear to be better absorbed than insoluble sources, employing cooking methods that significantly reduce soluble oxalate may be an effective strategy for decreasing oxaluria in individuals predisposed to the development of kidney stones.
Other sources of oxalates:
Bacteria: bacteria produce oxalic acid when digesting carbohydrates. This could be one of the factors contributing to IBS. Most people with IBS do better on a low carb diet. Could they be sensitive to oxalic acid?
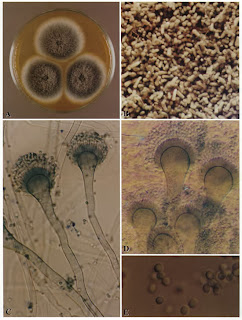
Aspgergillus (pictured above): this is a fungus that can wreak havoc on the respiratory system. Many people get chronic sinusitis, bronchitis, or asthma from overexposure to aspergillus. Aspergillus creates oxalic acid. High amounts of oxalic acid were found in the bronchiol lavages of people with aspergillosus lung infections.
Here in our office, allergy to oxalic acid sometimes comes up in muscle testing. Oxalic acid sensitivity cannot be tested by blood allergy tests. I have had several patients with interstitial cystitis show as sensitive to oxalic acid. Children who test sensitive have been given green smoothies--homemade smoothies with raw kale and spinach in them.
So remember, cook spinach and tough greens before eating them. If you insist on eating them raw, drink lots of water daily.
If you would like to get tested for sensitivities, call the office at 360-573-2273


No comments:
Post a Comment